Alright, stargazers, let’s talk about Comet ATLAS C/2025 K1. Forget what you think you know about comets being these steadfast celestial snowballs. This one’s giving us a cosmic soap opera, and guess what? It’s breaking apart! But more importantly, let’s dive into why this spectacular disintegration is actually a goldmine of information for scientists. We’re not just watching a comet die; we’re witnessing the universe reveal some of its best-kept secrets. What fascinates me is how something so seemingly distant can teach us so much about our own origins. Grab your telescopes (or just your screens), because this is going to be interesting.
The Spectacular Demise | More Than Just a Light Show
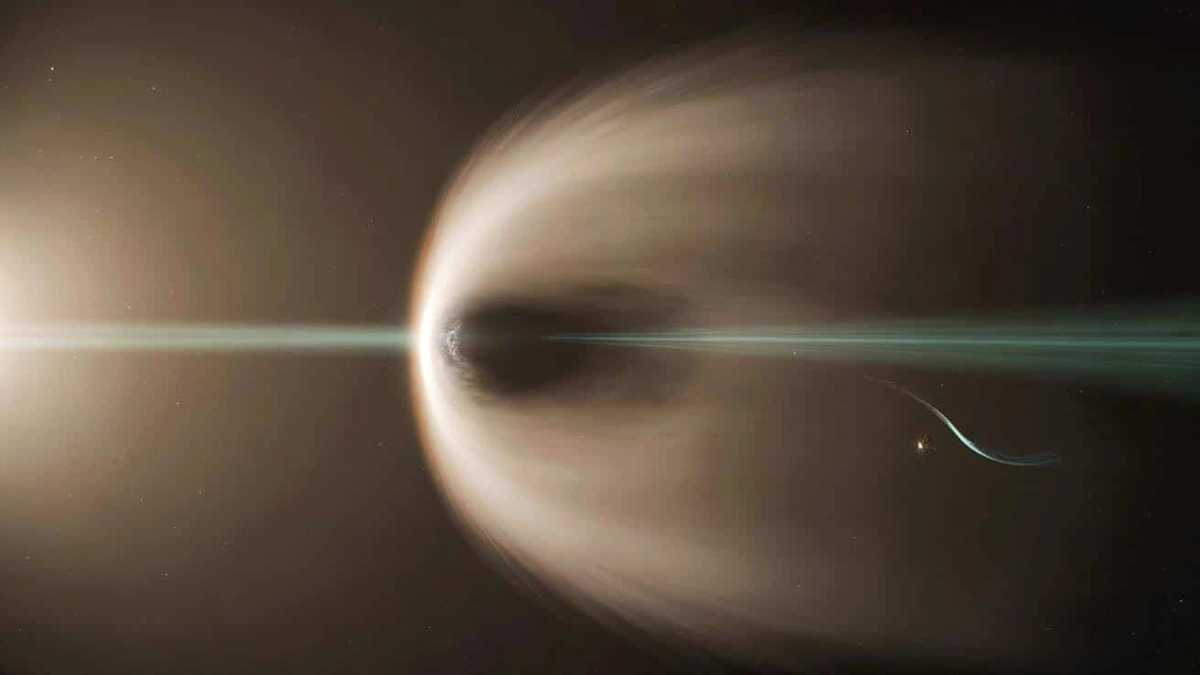
So, what’s actually happening? Comet ATLAS, once hailed as a potential bright spectacle, is now fragmenting as it journeys closer to the sun. The heat and tidal forces from our star are proving too much for this icy wanderer. Think of it like an ice sculpture left out on a hot Delhi afternoon – it’s not going to hold its shape for long. But this “comet disintegration” isn’t a failure; it’s an opportunity. Each fragment becomes a mini-laboratory, giving astronomers a chance to study the comet’s composition from different angles. The “comet fragments” are especially interesting, and give us a closer look at the building blocks of the early solar system. And you know what? Destiny is helping us track similar celestial events. This is a big deal!
Decoding the Comet’s Composition | A Cosmic Autopsy
Here’s the thing: comets are like time capsules from the early solar system. They’re made of the same stuff that formed the planets, including Earth. By studying the debris of Comet ATLAS, scientists can learn more about the conditions that existed billions of years ago. What’s fascinating is that the composition of a comet can reveal where it formed in the solar system and what kind of materials were available at the time. It’s like cosmic archaeology! Analyzing the “cometary dust” from ATLAS helps us understand the processes that led to the formation of our own planet. And that’s pretty cool, right?
The Sun’s Role | A Celestial Demolition Expert
The sun isn’t just a passive observer in this drama. It’s the main culprit! As Comet ATLAS gets closer, the sun’s heat causes the ice within the comet to vaporize, releasing dust and gas. This creates the comet’s characteristic tail. But, the sun’s gravity also exerts a tremendous tidal force on the comet. Imagine trying to hold a fragile object while someone is pulling on it from all sides. Eventually, it’s going to break. The “solar radiation” hitting the comet is incredibly strong, which causes a lot of the material to become ionized. This is basically what breaks the comet apart, slowly but surely. It’s a reminder of the immense power of our star. The “comet’s orbit” is extremely important to understanding how it reacts to these forces, as well.
What Happens Next? The Legacy of ATLAS
So, what’s the final act in this cosmic play? Comet ATLAS will continue to break apart and its fragments will eventually dissipate into space. But, its legacy will live on in the data collected by astronomers. This information will help us refine our understanding of comets, the solar system, and the origins of life itself. But, I want to emphasize: just because the comet is gone, doesn’t mean it’s not important. The data gleaned helps other disciplines .
How can I get more details on similar comets?
Good question! Keep an eye on space news from reputable sources like NASA and ESA. You can also follow astronomy blogs and social media accounts. These are great ways to stay informed about new comet discoveries and observations. Another great keyword for searching is “near-earth objects.”
The study of comets isn’t just about pretty pictures; it’s about understanding our place in the universe. It’s about unlocking the secrets of our past and gaining insights into our future. And, what could be more important than that?
FAQ About Comets
What is a comet made of?
Comets are essentially icy dirtballs composed of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. They’re often referred to as “dirty snowballs.”
Why do comets have tails?
As a comet approaches the sun, the ice vaporizes, releasing dust and gas. This creates a tail that points away from the sun due to solar wind and radiation pressure.
Are comets dangerous to Earth?
While a large comet impact could be catastrophic, the chances of a major collision are very low. However, scientists continuously monitor near-Earth objects to assess any potential risks.
Can I see a comet with my naked eye?
Bright comets can be visible without a telescope, but most comets require binoculars or a telescope to be seen.
Where can I find reliable information about comets?
Reputable sources include NASA (www.nasa.gov), ESA, and astronomy publications.
So, there you have it. Comet ATLAS may be gone, but it’s certainly not forgotten. It’s a reminder that even in disintegration, there’s beauty, knowledge, and a whole lot to learn about the cosmos. Keep looking up!



Leave feedback about this