Okay, let’s be honest – when we think of comets, we picture those icy wanderers zipping around the Sun in predictable, if elongated, paths. But every now and then, something throws a cosmic curveball. Enter Comet 3I/ATLAS, an interstellar interloper that’s got astronomers scratching their heads. It’s not just that it came from another star system, it’s the comet orbit itself that’s so darn peculiar. Why? Well, that’s what we’re diving into today.
What Makes Comet 3I/ATLAS So Weird?
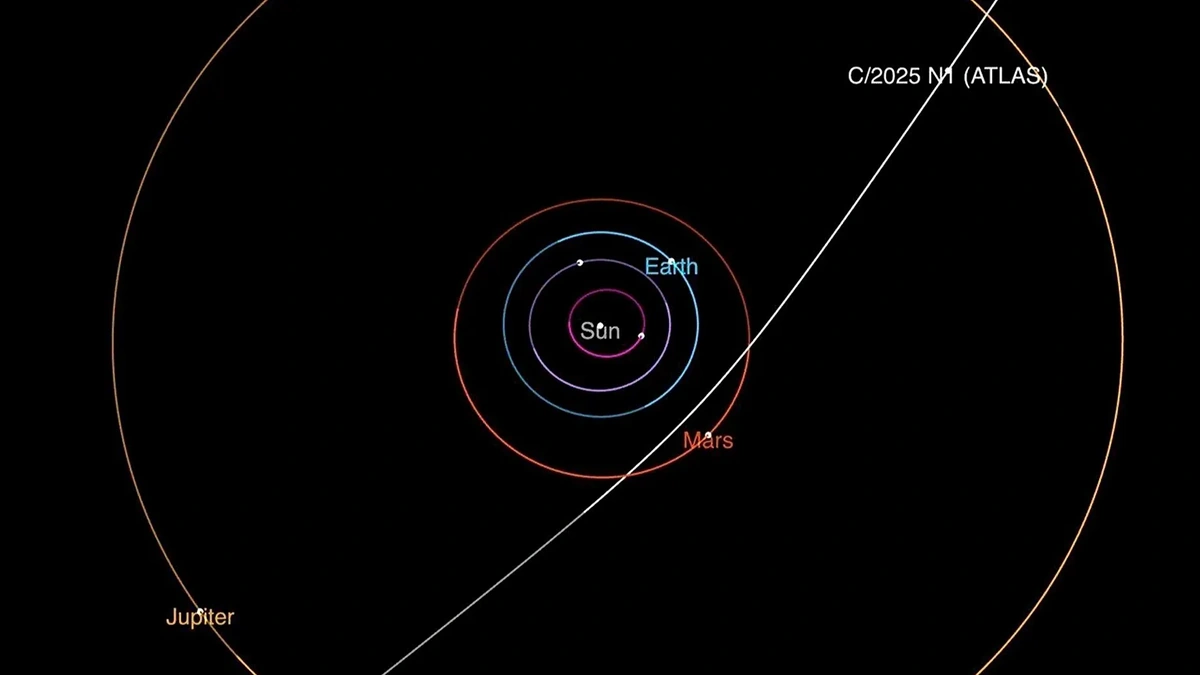
So, what fascinates me about 3I/ATLAS isn’t just its interstellar origin – although that’s definitely cool – it’s the sheer unlikeliness of its journey. Most comets reside in our solar system’s outer reaches, in the Oort cloud or the Kuiper belt. They might get nudged into the inner solar system by gravitational disturbances, but their orbits usually follow certain patterns. 3I/ATLAS? Not so much. Its trajectory suggests it’s been wandering the galaxy for billions of years before paying us a visit. To understand just how unusual this is, consider the typical cometary motion . Usually predictable, this comet has thrown scientists for a loop. Also consider the fact that interstellar objects rarely enter our Solar System, making this a significant occurence.
Here’s the thing: figuring out where it came from and how it got here involves some serious detective work. We’re talking about tracing its path backward through space, accounting for the gravitational influences of countless stars and planets. It’s like trying to figure out where a single raindrop originated after it’s been swept up in a hurricane. Complex? Absolutely. Impossible? Hopefully not!
Unraveling the Mystery of the Unlikely Orbit
The “how” of 3I/ATLAS’s orbit is where the real puzzle lies. It’s not just about calculating its trajectory; it’s about understanding the forces that shaped it. One key factor is the gravitational dance between stars in our galaxy. As stars move past each other, their gravitational fields can tug on objects like comets, altering their paths. But for 3I/ATLAS to have ended up on its current trajectory, it would have required a series of extremely precise gravitational encounters. And that’s what makes this whole thing so improbable.
I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized how many variables are at play. Consider the potential influence of dark matter, the mysterious substance that makes up a significant portion of the galaxy’s mass. While we can’t directly see dark matter, its gravity could have subtle but significant effects on the orbits of interstellar objects. This is a key factor when considering the gravitational influence on comets . According to research, understanding its effect could change how we understand space as a whole. Planetary defense from space objects has become even more important than before, as we learn more about these interstellar travelers.
What Does 3I/ATLAS Tell Us About the Galaxy?
So, why should we care about one weird comet? Because 3I/ATLAS is more than just a space rock; it’s a messenger from another star system. It carries with it clues about the composition and conditions of the environment where it formed. By studying its chemical makeup, we can learn about the building blocks of planets in other solar systems. Think of it as a cosmic time capsule, delivering insights from a distant past.
And here’s where it gets really exciting. If 3I/ATLAS is representative of other interstellar objects, it suggests that such objects may be more common than we thought. This has profound implications for our understanding of how planets and even life might spread throughout the galaxy. The presence of interstellar comets like 3I/ATLAS could mean that the building blocks of life are more widely distributed than we previously imagined. You could even say it opens the door for understanding comet fragmentation and its effects on space travel.
The Future of Comet Research and Our Understanding of Comets
The discovery of 3I/ATLAS has spurred a new wave of research into interstellar objects and the dynamics of the galaxy. Astronomers are developing new models to predict the paths of these objects and to understand the forces that shape them. Future space missions may even be dedicated to studying interstellar objects up close, providing us with a wealth of new data. It is possible we will be able to predict the future of cometary research with more powerful technology.
But, as always, there are challenges. Interstellar objects are rare and often faint, making them difficult to detect and study. And even with the most powerful telescopes, it’s impossible to know everything about their origins and histories. But that’s part of what makes this field so exciting. It’s a constant process of discovery, with new surprises and challenges around every corner.
As per the guidelines mentioned in the information bulletin, researching comets will become easier with the James Webb Space Telescope, giving us a clearer, more concise, view of space. With better visibility, predicting the trajectory analysis for comets will become easier and more reliable.
Is Comet 3I/ATLAS a Threat to Earth?
Let’s address the elephant in the room: is 3I/ATLAS a threat to Earth? The short answer is no. Its orbit takes it nowhere near our planet. But the fact that it could have, in some alternate scenario, makes you think. That’s where initiatives for near-earth object detection come into play.
The one thing you absolutely must double-check is that the research being done by astronomers has led to more refined models, ensuring future predictions will be more accurate. In the grand scheme of things, 3I/ATLAS is a reminder of the vastness and complexity of the universe and the many wonders that await us. This comet is an example of how the galaxy is much more dynamic and interconnected than we thought!
FAQ About Comet Orbits
What is an interstellar object?
An interstellar object is a celestial body, such as a comet or asteroid, that originates from outside our solar system.
How do astronomers detect interstellar objects?
Astronomers detect interstellar objects by analyzing their trajectories, which are often hyperbolic (open) and indicate that they are not gravitationally bound to the Sun.
What can we learn from studying interstellar objects?
By studying interstellar objects, we can learn about the composition and conditions of other star systems, as well as the processes that shape the galaxy.
Are interstellar objects dangerous to Earth?
While some interstellar objects could potentially pose a threat to Earth, most are too small or too far away to be of concern. Continuous monitoring and research is being conducted to detect and assess potential risks.
Ultimately, the story of Comet 3I/ATLAS is a reminder that the universe is full of surprises, and that there’s always more to discover. It’s also a testament to the power of human curiosity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge. And, you know, that’s pretty awesome.



Leave feedback about this